What we research
1. Interactions of metal ions with ligands and clusters
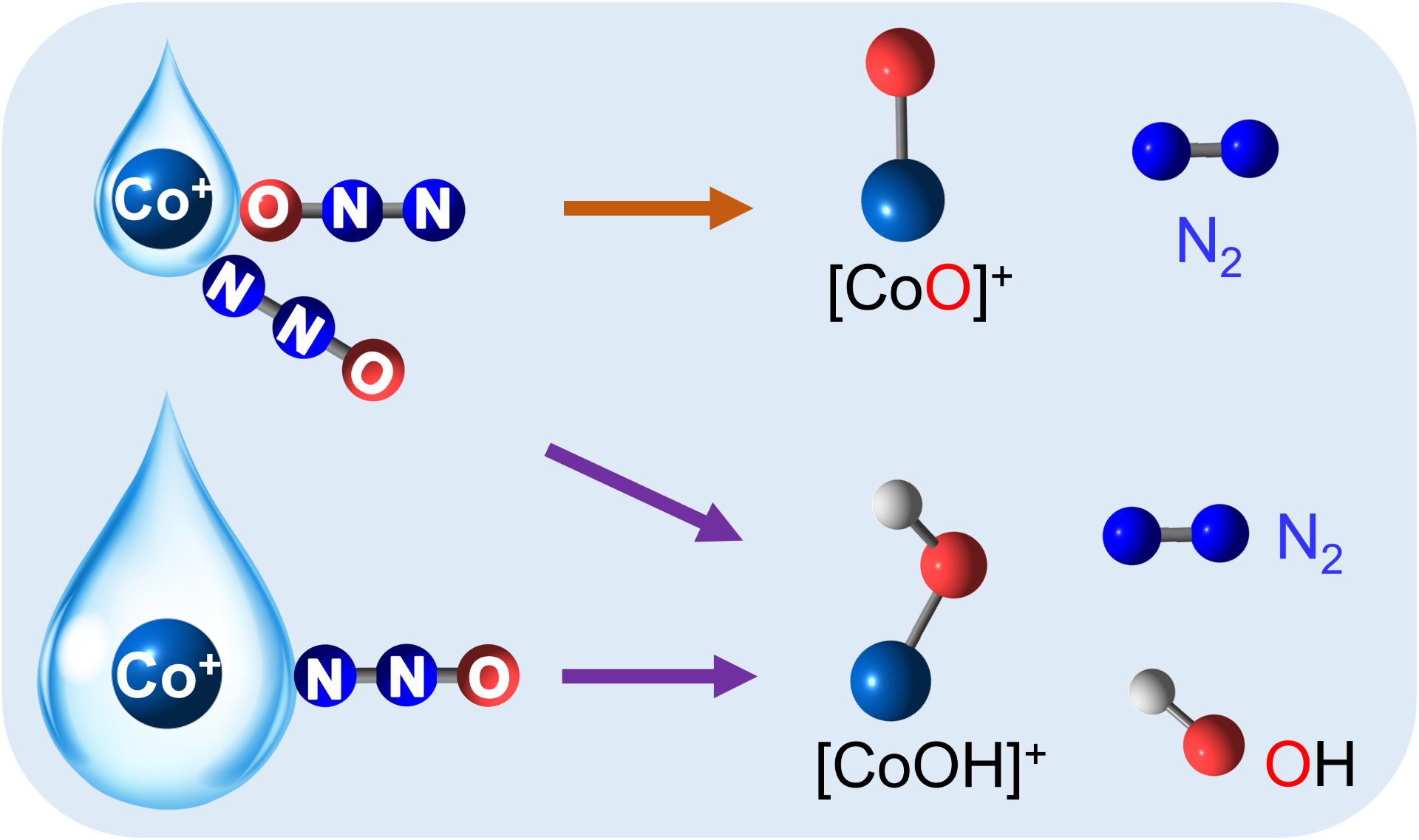
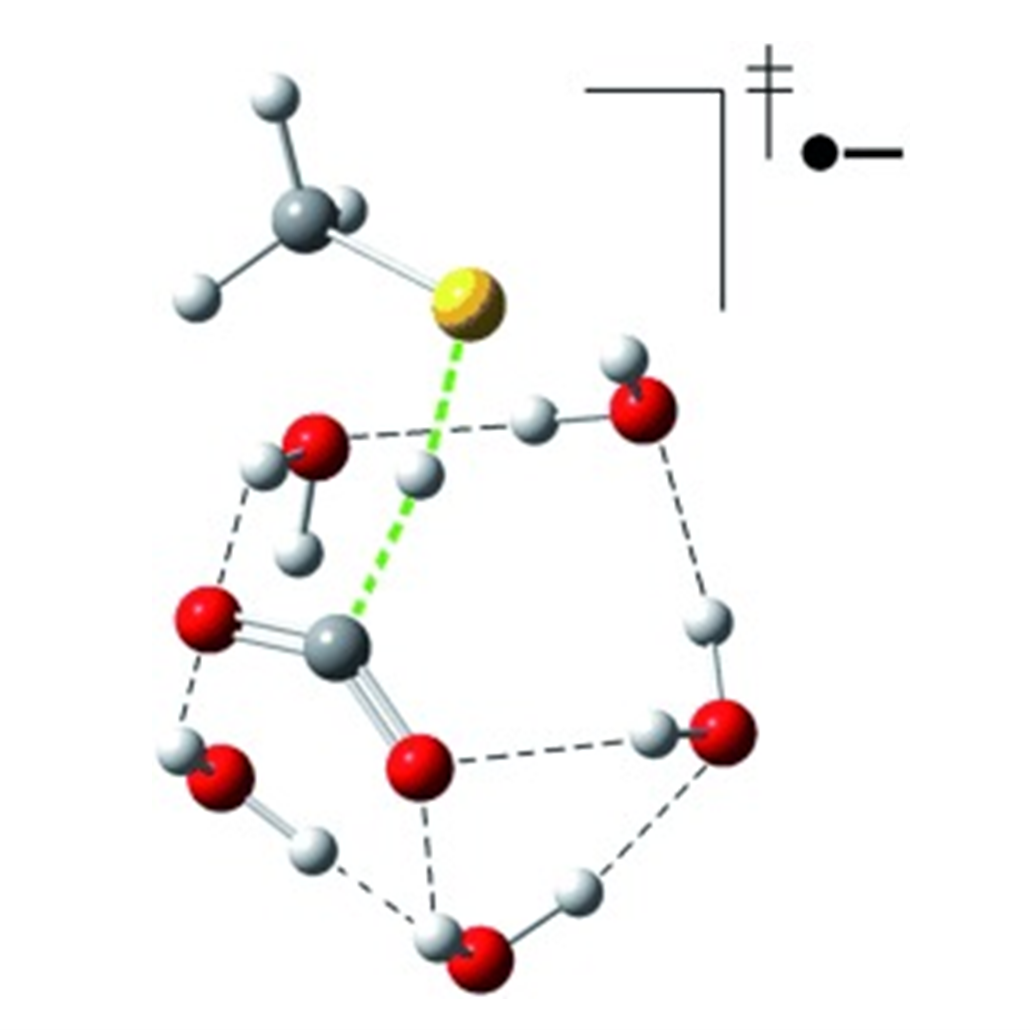
Hydrated metal ions in the gas phase serve as model systems to study key chemical reactions, e.g., hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and nitrous oxide decomposition. Under different degrees of hydration, chemical reaction at the metal centres could portray different reaction pathways.
Catalysis involving first-row transition metals activated by tailor-made ligands is a thriving field due to their lower cost and toxicity as compared to their heavier congeners. Microsolvated metal ion clusters are used as prototypical models to study intrinsic properties of metal complexes.
2. Dynamic solute-solvent interactions on charge transfer phenomena
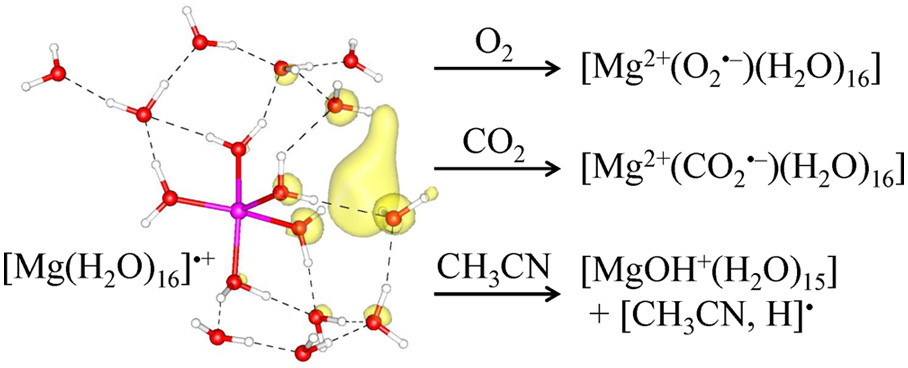
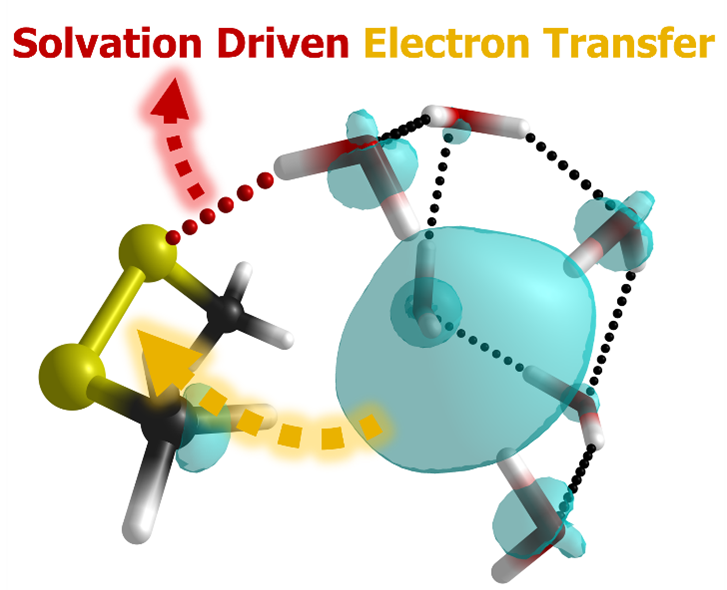
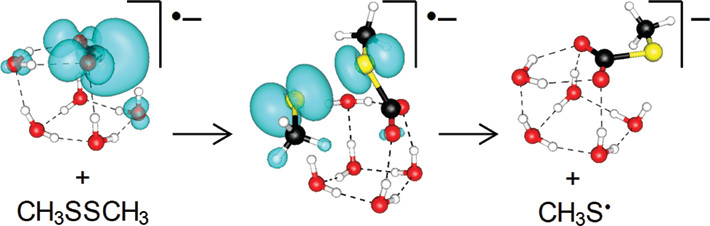
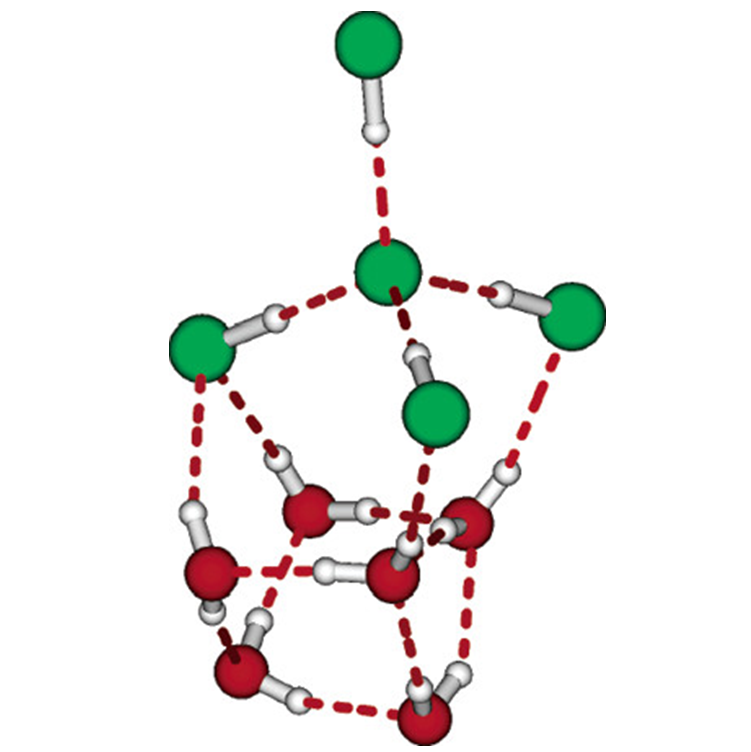
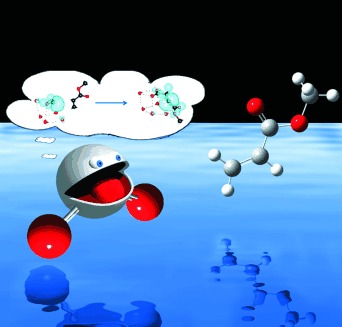
Under sufficient hydration, specific metal centres generate hydrated electron after charge separation. Reactivity of hydrated electron and questions about its unique behaviour has persisted since its discovery in 1962. Reductions of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acetonitrile, and prototypic organosulphur compounds are investigated for their charge transfer mechanisms.
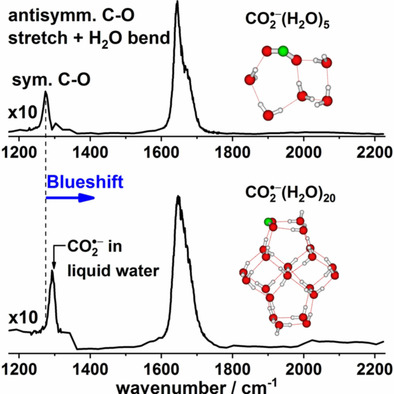
Another interesting charge carrier (i.e. carbon dioxide radical anions) is of our interest as understanding the intrinsic properties is relevant for electrochemical carbon dioxide functionalization. For example, its radical anion can be utilized as one-carbon building blocks in organic synthesis for selective formic acid synthesis.
3. Imitating charge transfer processes in biological systems
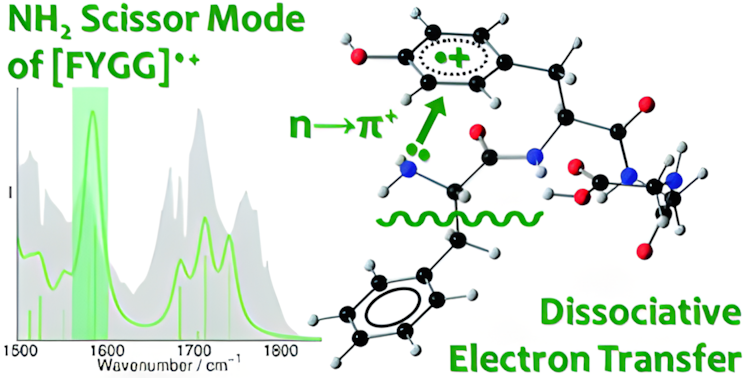
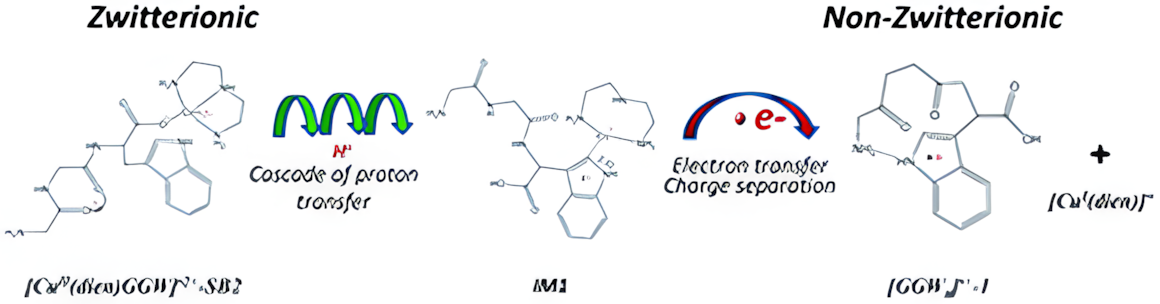
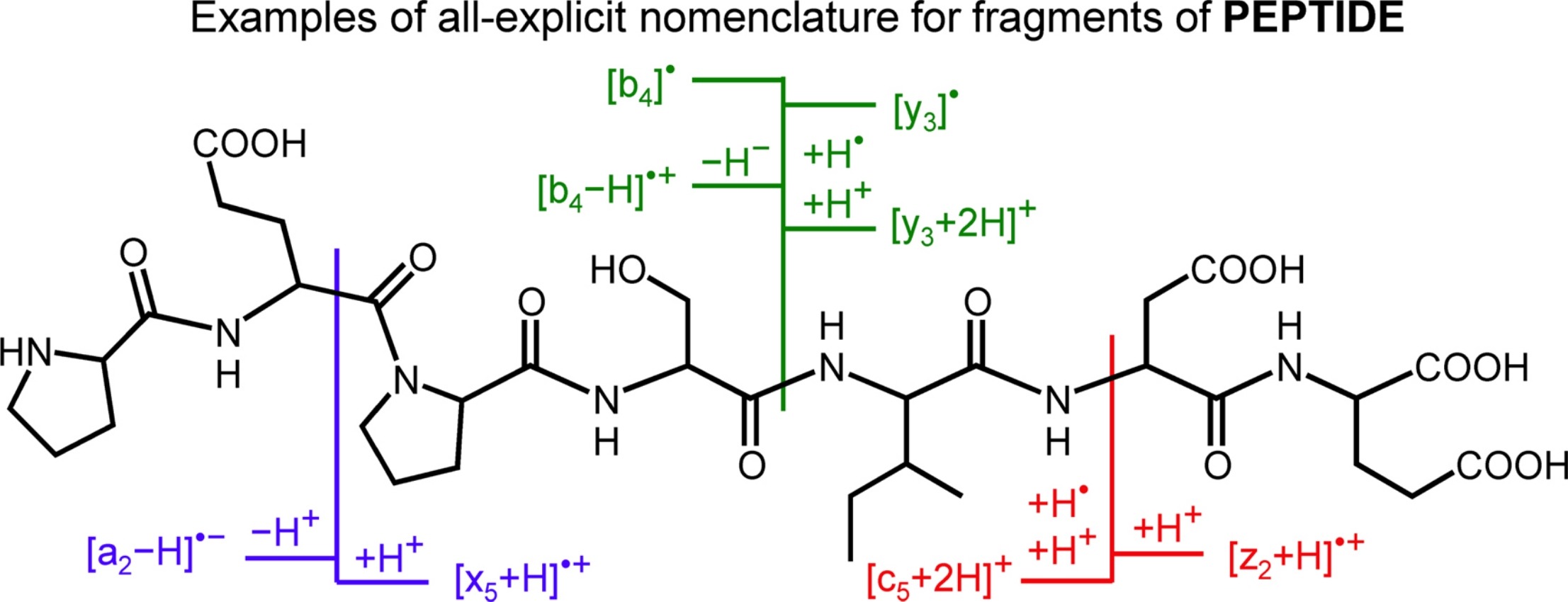
Electron transfer in proteins governs many important biological processes, such as photosynthesis, free radical damage and charge transport. Particularly, electron hopping can rationalize charge transport up to submicron distances, over which tunneling is inefficient. Model tripeptide cations are used to probe α- and π-radical migrations in sequential redox processes via amino acid residues.
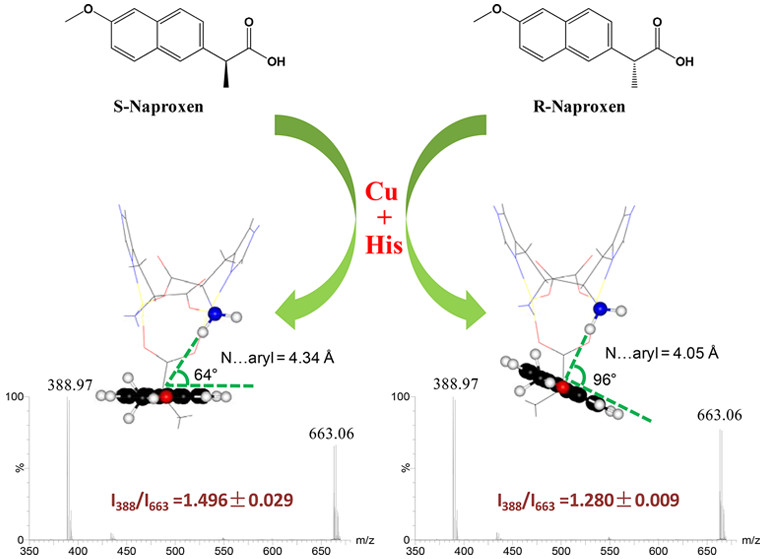
Chiral recognition by mass spectrometry on the introduction of a chiral selector is superior in speed, sensitivity and specificity compared to chromatography. Discrimination of enantiomers is achieved by dissociation efficiency in MS/MS or drift time in IM-MS due to different binding behaviours with chiral selectors.
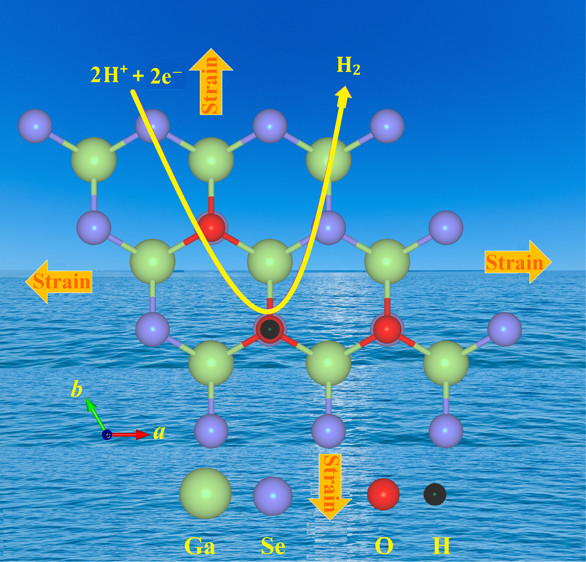
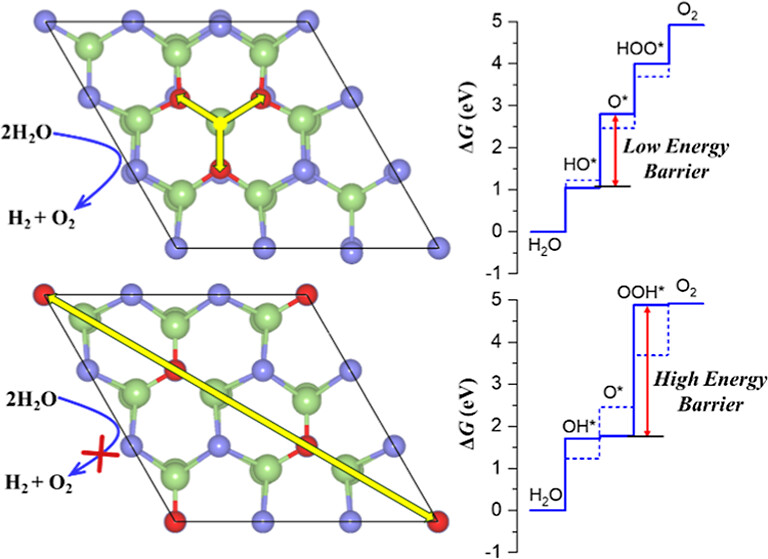
4. Modeling 2D materials for water splitting reaction
A single-layer of GaSe is widely regarded as one of the most promising photocatalysts for a solar-driven water-splitting reaction. Partial substitution of Se with O atoms can improve its catalytic efficiency. Different atomic configuration of O dopants shows varying energy barrier towards both hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen evolution reaction.